The Economic Impact of Grab in Singapore
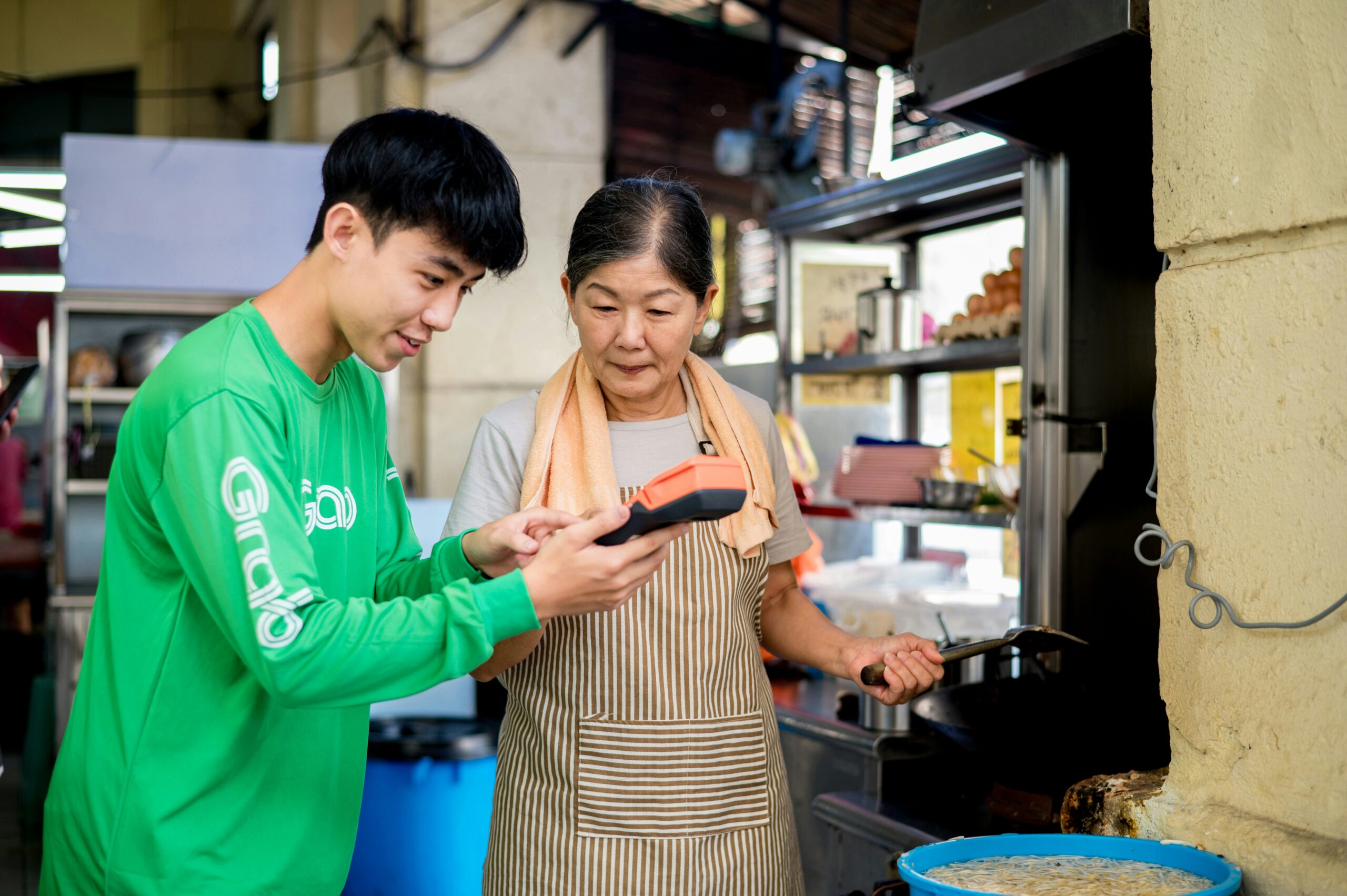

Since its establishment in 2012, Grab has rapidly evolved into a cornerstone of Singapore’s digital economy, catalysing innovation, and transforming the daily lives of millions of citizens through its “super-app”.
Our analysis suggests that Grab’s on-demand services, namely its ride-hailing and delivery, facilitated a total economic contribution worth S$5.2 billion to the Singaporean economy in 2023, supported 117,000 earning opportunities, and generated S$2.5 billion in household income. This impact is generated through purchases on the app and the economic activity it supports among the local supply chains in the wider Singapore economy.
For every employee hired by Grab, an extra six workers are supported in other parts of the Singaporean economy. Every S$10 of GDP generated by transactions on the Grab platform for on-demand services, leads to further economic activity worth S$6 of GDP across the rest of the Singaporean economy.
Beyond its direct economic contributions, Grab also connects driver-, delivery-, and merchant-partners to the digital economy, creating new pathways for income generation and economic participation.
The experts behind the research
Our Economic Consulting team are world leaders in quantitative economic analysis, working with clients around the globe and across sectors to build models, forecast markets and evaluate interventions using state-of-the art techniques. Lead consultants on this project were:

Bali Kaur Sodhi
Lead Economist, Economic Impact

Hwee Shi Yong
Assistant Economist, Economic Impact
Tags:
You might be interested in

Inside the UK’s Data Centre Boom: Why London Still Dominates—and what comes next
As AI accelerates and global tech companies commit billions to new cloud and data-centre projects in the UK, the country is cementing its role as a leading AI hub.
Find Out More
Powering the UK Data Boom: The Nuclear Solution to the UK’s Data Centre Energy Crunch
The UK’s data centre sector is expanding rapidly as digitalisation, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence (AI) drive surging demand for high-performance computing infrastructure.
Find Out More
Measuring the Value of Design in Singapore
This study explores how design delivers value to Singapore-based organisations, enhancing profitability, strengthening strategic performance, and supporting broad environmental and social benefits. It introduces a Theory of Change framework to help organisations more effectively communicate and measure the value of their design activities.
Find Out More
Flooding risks diverge across UK cities, sectors and economies
Climate-linked flooding is becoming more severe, reshaping risks for UK cities, real estate, and local economies. Which areas face the greatest impact—and why?
Find Out More