Blog | 29 May 2024
Government bonds will not return as diversifiers soon

Alessandro Theiss
Director, Financial Modelling and Scenario

With the May update of our Global Economic Model, we added government bond total return indices for a selection of countries and regional aggregates. This model enhancement allows users to easily gauge our baseline forecast for government bond returns, and how these vary in alternative scenarios. Our modelling framework also allows users to understand which factors are most important in driving these return projections.
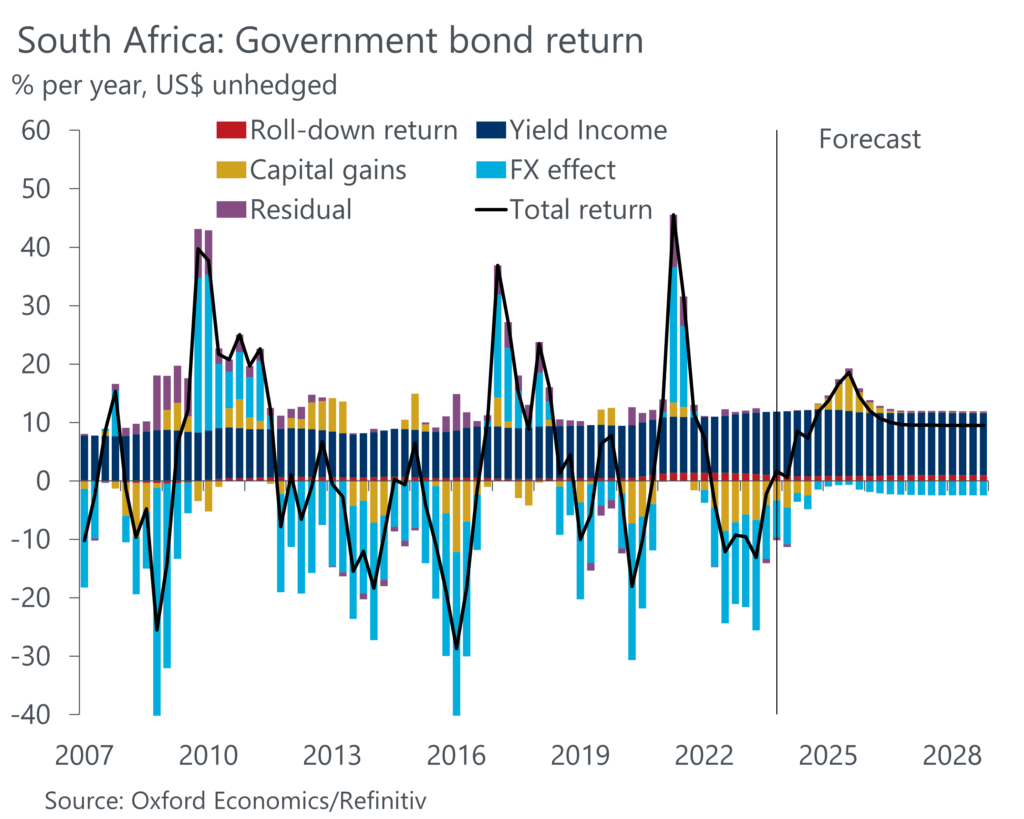
A decomposition into capital gains, yield income (coupon payments), and roll-down return shows that for many advanced economies (AEs) our upbeat return expectations are predicated on yields falling back from their current elevated levels. For emerging markets, structurally high interest rates provide a healthy cushion for returns, while the relative contribution from capital gains to total returns is generally more limited. But the rollercoaster of US rate expectations and a strong US dollar will continue to skew the risk-reward profile for investing in EMs.
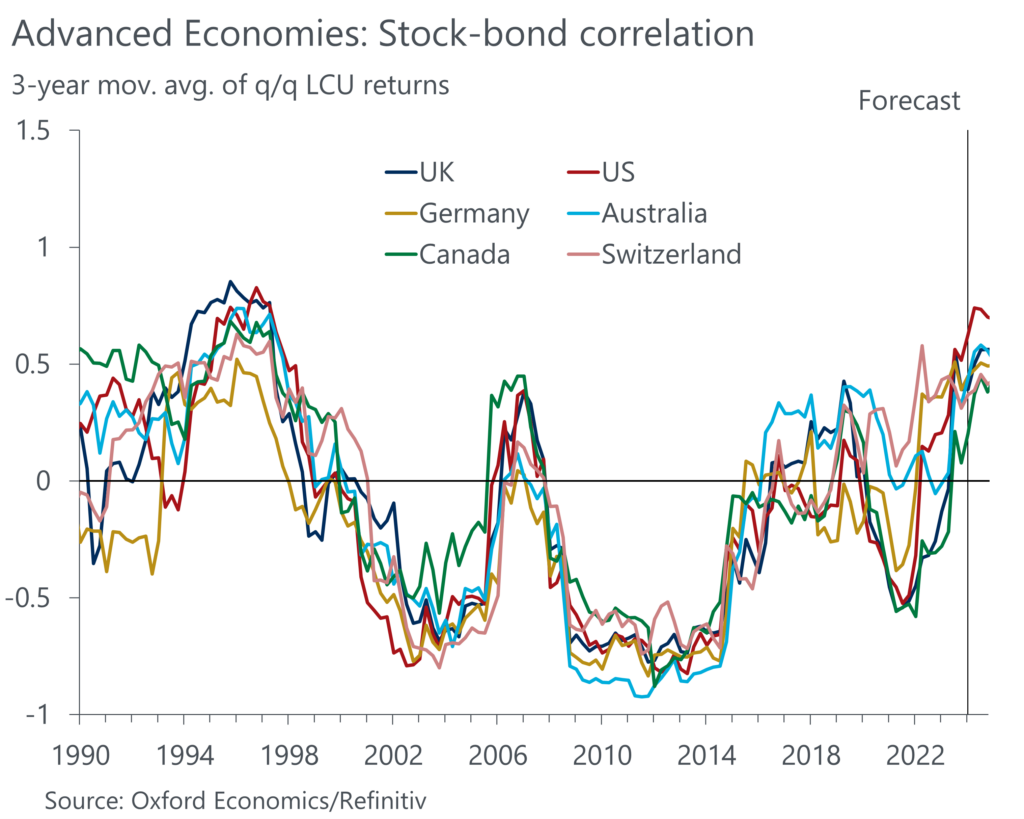
Beyond considerations around the magnitude and volatility of expected returns from an asset class, investors need to worry about the correlation between returns from the various asset classes held in their portfolios. This enables them to shield their portfolios from excessive losses during episodes of market distress. The correlation between equity and government bond returns is particularly important in this context, as these two asset classes generally account for the largest shares in traditional portfolios.
The striking commonality of the stock-bond correlation (SBC) across AEs can be explained by many of the factors affecting the SBC being determined as much by global development as by domestic ones. For example, the period following the Global Financial Crisis, during which the SBC was strongly negative, was characterised by low and stable inflation and interest rates, fiscal consolidation to repair public balance sheets, and an absence of large global supply shocks. These driving forces have all been upended in the aftermaths of the Covid-19 pandemic. In response, the SBC became strongly positive, reducing the hedging properties of government bonds and the risk-reward profile of a standard investment portfolio.
It seems likely that the SBC will remain positive and elevated for several reasons. Central banks’ fight against inflation is not fully over and more shifts in central bank reaction functions can be expected. As a result, uncertainty about the future path for interest rates will remain elevated which is supportive of a positive SBC. Furthermore, we expect that geopolitical instability and a more extreme climate will cause more supply shocks in the future, increasing inflation volatility and keeping risk premia elevated.
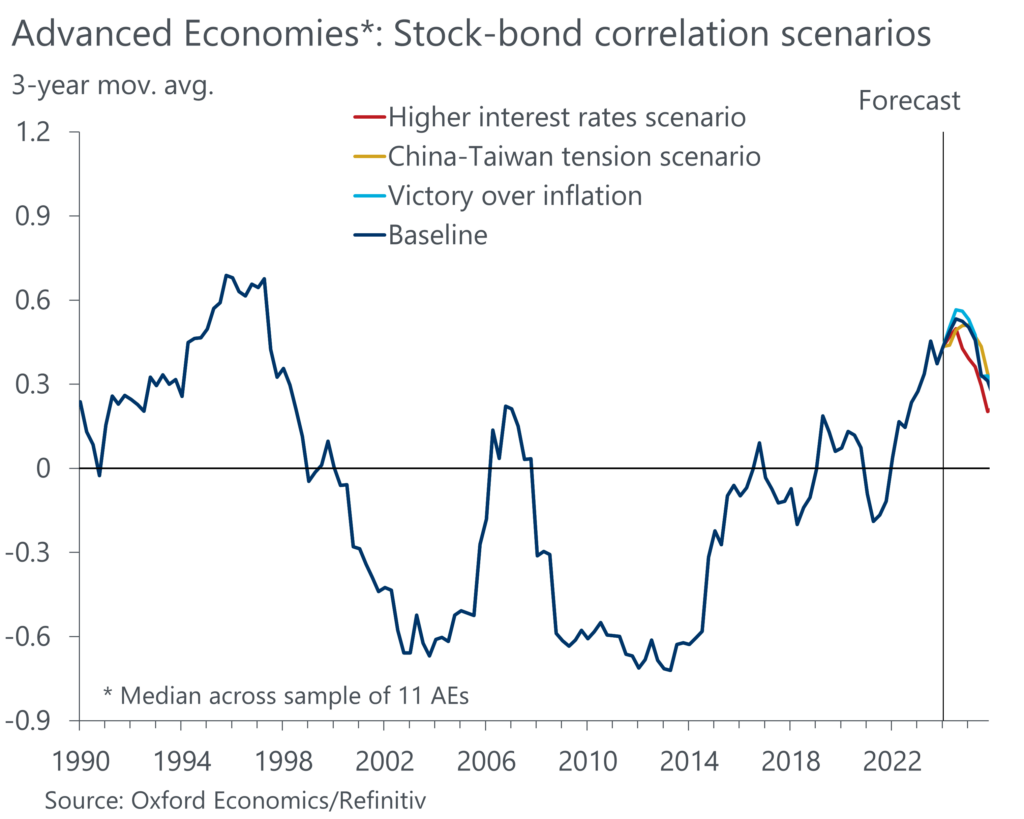
Indeed, when assessing the implied predictions for the SBC from our Global Economic Model across a range of alternative scenarios, we generally find little scope for a reversal to a negative correlation in the near term. This does not only hold true in our downside scenarios but also in our upside scenario, where inflation is brought under control faster than what we expect in our base case forecast. While a traditional investment portfolio would see higher returns than in the base case in this scenario, bonds would still not act as diversifiers.
Tags:
You may be interested in

The Green Leap: More promises but little innovation at COP30
The COP30 in November made some ambitious commitments to scaling up climate finance. Until those materialise, initiatives to leverage natural endowments for financing may be more attractive to African countries, especially those with high forest cover.
Find Out More
The Green Leap: Unlocking climate financing at COP30 for Africa
The scaling of climate finance for developing countries will take centre stage at the 30th Conference of the Parties (COP30) of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) starting today, in Brazil. Leaders will grapple with how to plug the gaping shortfall in funds needed to help developing economies curb emissions and adapt to climate shocks. Reforming the global financial architecture will be a key discussion.
Find Out More
Continental oil kings missing out on evolving oil dynamics
Uncertainty around global growth has widened the range of possible outcomes for oil consumption. While demand growth currently lags behind supply, stronger-than-expected trade or industrial activity could lift demand above projections. This brief explores whether Nigeria and Algeria are positioned to take advantage of such an upside.
Find Out More
Cameroon election: Change, but when?
Cameroon’s President Paul Biya is expected to secure another term in the upcoming presidential election.
Find Out More