Blog | 17 May 2022
The Russia-Ukraine war: Three key dependencies affecting European industry

Industry Services Team
Oxford Economics

Russia’s huge oil and gas reserves, and the systemic importance of some commodities that are exported by Ukraine make the two countries a key part of the global supply chain. Europe in particular is heavily reliant on Russia for its energy needs, with 27% of EU total crude oil imports and 41% of total EU imports of natural gas coming from Russia (Chart 1). To understand how the Russia-Ukraine war might affect European industry, we have investigated three key channels through which the economic impact of the war will be felt.
Chart 1: Russia in the World Economy
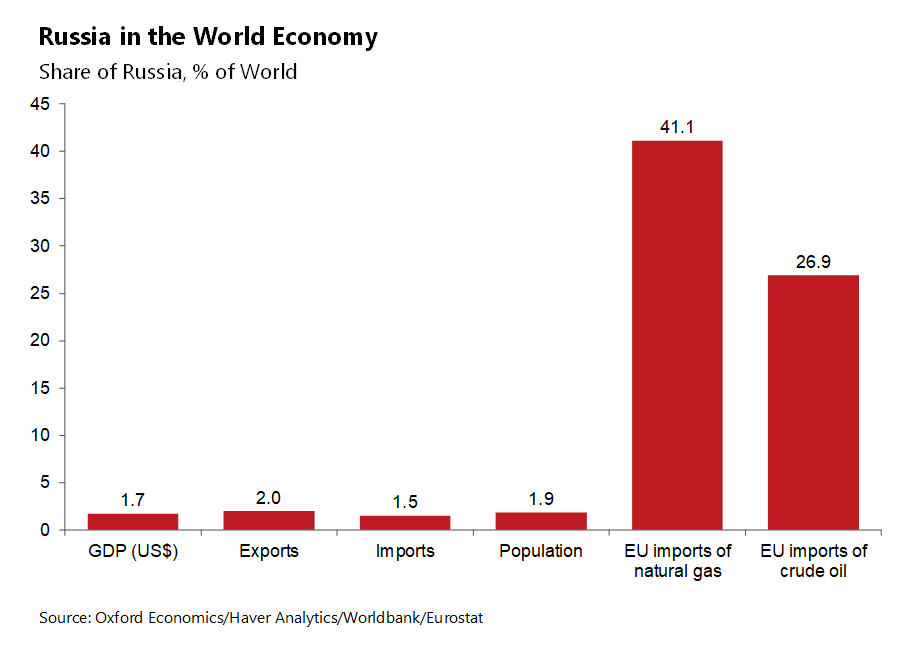
- Dependency on Russian gas
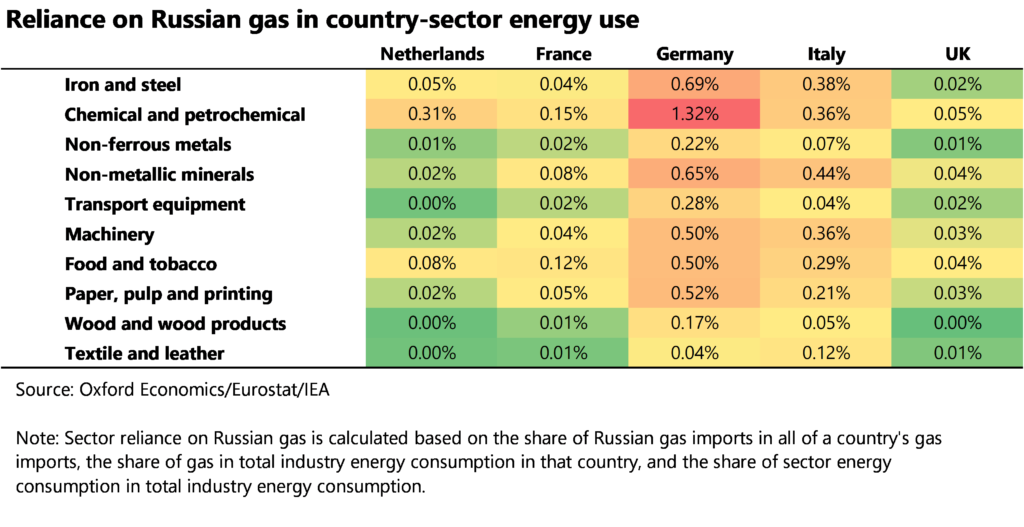
Immediately following the Russian invasion in late February, Brent oil prices reached their highest levels since 2014, while European natural gas prices skyrocketed. The negative impact on European industries is two-fold: Surging energy prices have caused inflation rates to climb to levels not seen in decades, squeezing real household incomes and hence consumption demand. Meanwhile, production costs have increased sharply. Table 1 aims to capture country-industry exposure to the latter. Sectors that are more energy-intensive (notably, iron and steel and chemicals production) and are located in countries with a stronger dependency on Russian gas imports (notably Germany and Italy) are likely to be more exposed to rising energy prices and changes in gas supplies by Russia.
Table 1: Reliance on Russian gas in country-sector energy use
- Dependency on Russian intermediate inputs
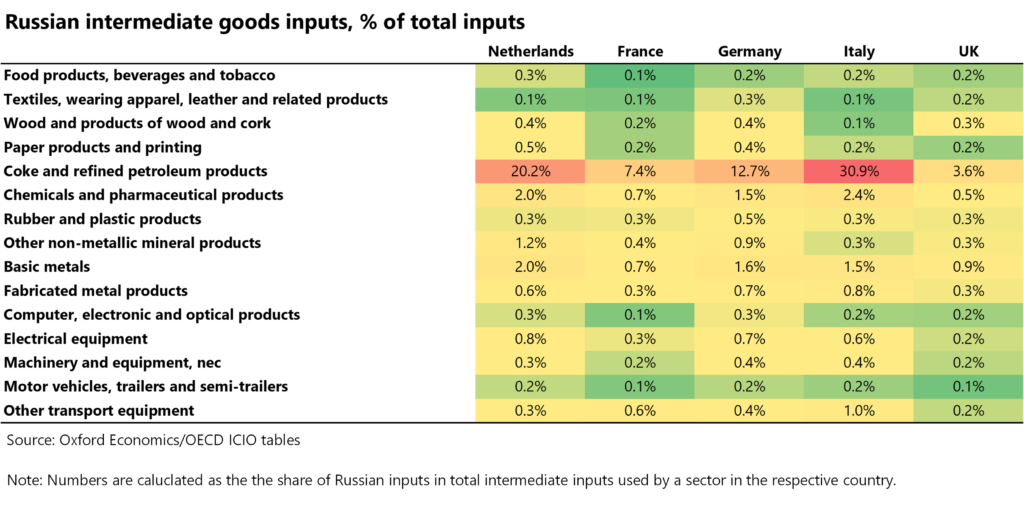
Following the invasion, the European Union, US, UK, Canada and other countries imposed a range of economic and financial sanctions on Russia that include export and import restrictions to and from Russia. Sectors with a strong direct dependency on Russian intermediate inputs are more likely to experience supply chain bottlenecks due to these sanctions or other logistics and transportation disruptions caused by the war. Table 2 shows that the dependence on Russia is concentrated in upstream sectors of the supply chain, reflecting the resource-intensive nature of European economies. The coke and refined petroleum producing sector stands out as the most vulnerable.
Table 2: Russian intermediate goods inputs as a share of total inputs
- Dependency on Ukrainian intermediate inputs
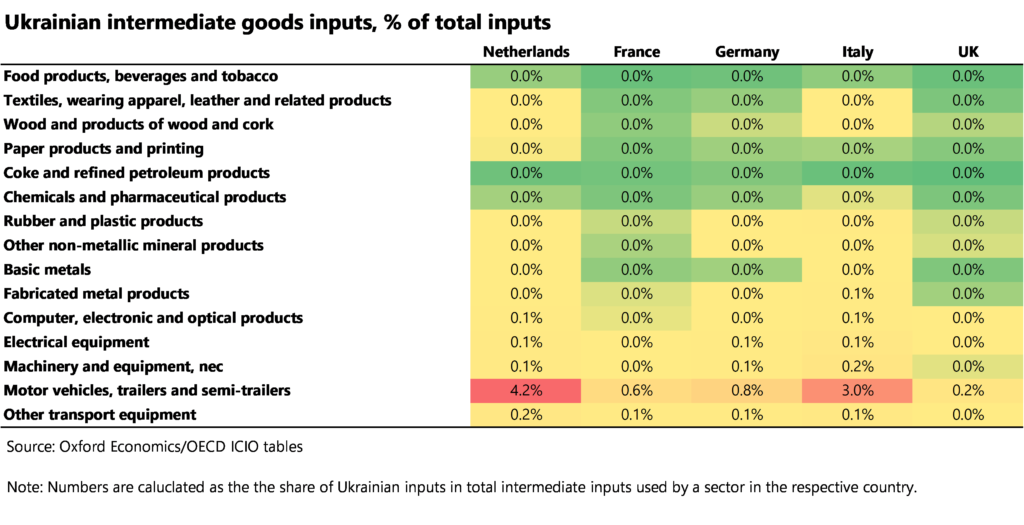
Similarly, sectors with a strong direct dependency on Ukrainian inputs are more likely to experience supply chain bottlenecks resulting from a drop in output of exported goods due to plummeting production and an inability to transport them. Table 3 shows that direct supply chain linkages between Europe and Ukraine are smaller than with Russia, but there are some potential pinch points—in particular, the European automotive sector shows the greatest degree of vulnerability. Although the share of intermediate inputs sourced from Ukraine is small in absolute terms, there seem to be very specific pockets within supply chains that have a higher exposure to the crisis. For instance, following the Russian invasion, German carmakers VW, Porsche, and BMW had to suspend production as war disrupted the supply of wire harnesses from Ukraine.
Table 3: Ukrainian intermediate goods inputs as a share of total inputs
While these pressures are not yet quantifiable, further disruptions brought about by firms’ inabilities to procure a specific part are likely to emerge over the coming months. The prospect of further sanctions and turmoil in commodity markets means that risks are heavily skewed to the downside.

Alexandra Hermann
Lead Economist, Asia Macro
+44 (0) 203 910 8042

Alexandra Hermann
Lead Economist, Asia Macro
London, United Kingdom
Alexandra is a Lead Economist on the Industry team where she is responsible for sectoral forecasts for the chemicals and pharmaceuticals industry and helps develop the team’s view on the global industrial outlook. She has also supported macroeconomic consulting projects such as developing scenario analyses for Accenture. Her role also involves contributing to bespoke industry consulting projects across a range of sectors such as chemicals, machinery, and energy.
Prior to joining Oxford Economics, Alexandra worked as an economic consultant for Cornerstone Research for over two years. At Cornerstone Research, she was involved in conducting qualitative research and quantitative analyses to support expert testimony in high-stakes litigation cases across a variety of sectors including energy, pharmaceuticals, and financial markets. Alexandra holds an MPhil in Economics from Oxford University and a BSc in Economics from the University of Mannheim. Alexandra is fluent in English and German.

Kiki Sondh
Economist
+44 (0) 203 910 8136

Kiki Sondh
Economist
London, United Kingdom
Kiki is a macroeconomist in the Global Macro team in London. She is responsible for producing macro research at a global level and managing the global macro forecast round. Previously Kiki worked on the Global Industry team, generating forecasts and providing narratives for the transportation and logistics sector. She was also engaged in various consultancy projects and industry research.
Prior to joining Oxford Economics in 2021, Kiki worked at the company in 2016 as part of her industrial placement year. During her 13-month internship, Kiki was responsible for macroeconomic forecasts for several countries and industry forecasts for the intermediate goods sector.
Kiki holds an MSc in Economics from the London School of Economics and Political Science and a BSc in Economics with Industrial Experience from the University of Exeter.
Tags:
You may be interested in

Post
Tariffs and Their Global Impact: A Note from the Desk of our Chief Economist
On 2 April 2025, the US Administration announced a set of tariff increases, bringing the US back to levels of protectionism last seen in the Great Depression era. This significant shift in trade policy is set to have far-reaching implications for the global economy.
Find Out More
Post
Nature scenarios: What changing environmental risks mean for businesses
Quantifying the economic impacts of nature change means considering double materiality; economic activities can both impact and depend on nature.
Find Out More
Post
Trump tariff turbulence threatens global industrial landscape
Trump has moved swiftly to advance a trade agenda that goes beyond what was promised in the campaign. This will have a major impact on global industrial prospects.
Find Out More
Post
Four steps to ensure corporate sustainability programs are actually sustainable
Sustainability is a long game. Here are four steps to ensure your sustainability programs are actually sustainable.
Find Out More