Chartbook: what’s next for China in 2023?
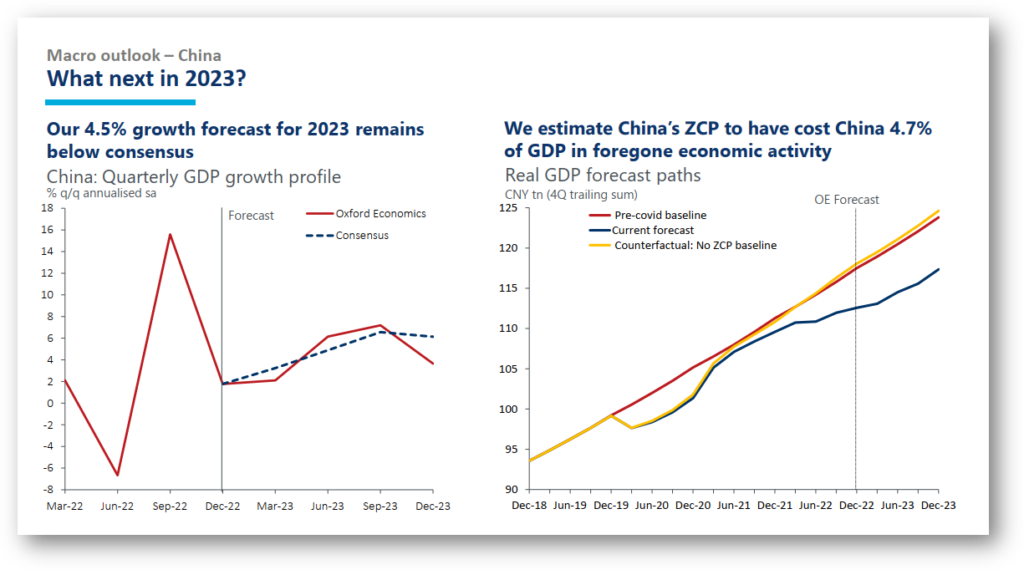
While China’s sooner-than-expected reopening has led some to pencil in a more robust rebound in 2023, we are more cautious. Our 4.5% growth forecast for 2023 remains below consensus.
What you will learn:
- The good news is that there are now tentative signs of stabilisation, as policy support doled out towards the end of 2022 showed up in the relative resilience of infrastructure investment and credit growth. The better news is that authorities will want to do more, and we see continued policy accommodation, primarily through off-budget fiscal channels in 2023.
- The bad news is that intrinsic drivers of the economy remain anaemic and in the longer term, structural challenges continue to cloud the economic outlook. Total population declined for the first time in 2022 since 1961, underscoring policymakers’ overarching productivity challenge.
- Our proprietary model estimates that China’s zero-Covid policy over the past three years has cost the economy 4.7% of its GDP in foregone activity.
Tags:
Related Resources


Post
Rise of new megacities will drive global urban growth
The population of the world's 1,000 largest and most important global cities is forecast to increase by more than half a billion by 2050. However, this urban demographic growth is not equally distributed across the world's cities.
Find Out More
Post
Chinese Outbound Travel to Gain Momentum in 2024
Chinese outbound travel finally restarted in 2023. This re-opening was keenly anticipated by global destinations, given the significance of China as an outbound market. Chinese outbound travel will stride further towards recovery in 2024.
Find Out More