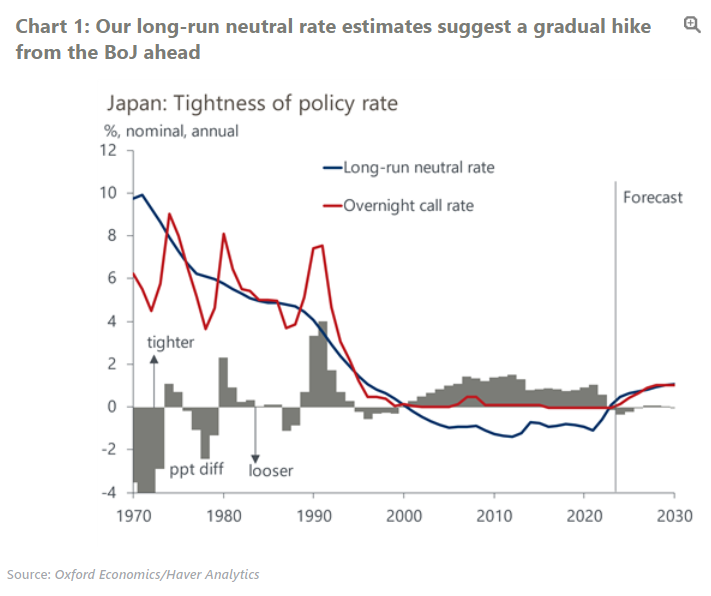
Japan’s neutral interest rate is rising, but not by much
We estimate that Japan’s nominal neutral interest rate – the rate consistent with monetary policy that is neither stimulative nor restrictive – has risen somewhat since 2022, marking a striking reversal from its decades-long slide. More importantly, we project it to continue rising gradually, to around 1% by 2030 from 0% in 2023.
What you will learn:
- Higher inflation expectations are one of the main reasons behind the recent increase in the nominal neutral rate. We believe that inflation expectations will continue to slowly edge up in the coming years amid robust wage gains, contributing to the projected neutral rate’s rise.
- Stripping out inflation expectations, the real neutral rate has risen only modestly in recent years. We think Japan’s demographic headwinds and weak productivity growth all but banish a sustained return to positive real neutral rates throughout our forecast to 2050. But in the next few years, increases in net foreign assets and the Bank of Japan’s step down in quantitative easing are likely to drive the rate slightly higher.
- Neutral rate estimates are inherently uncertain. Still, our approach provides a framework that can inform our view of the path for long-run interest rates, and our sensitivity and scenario analyses offer a useful gauge of the risks around our estimates.
Tags:
Related Posts

Post
Japan’s on course for July rate hike, but risk of June increases
The Bank of Japan (BoJ) kept its policy rate at 0.50% at Wednesday's meeting, as expected. Despite a marginally higher increase in pay than last year at the first round of the spring wage negotiations, our baseline view is for the BoJ to hike its policy rate only gradually due to concerns about the capacity of small firms to raise wages and the lacklustre rate of consumption.
Find Out More
Post
Japan’s supply-driven food inflation to persist longer than expected
We have revised our CPI forecast upwards for this year and next, due to more persistent supply side-driven food inflation, led by soaring prices of rice. Despite the significant revision to the short-term inflation path, we don't expect the Bank of Japan (BoJ) to react with a rate hike.
Find Out More
Post
Japan’s older households to support spending under higher rates
The resilience of consumption is essential to support sustained wage-driven inflation and the Bank of Japan's rate hikes. We see little risk of spending faltering due to the projected gradual rate hikes to 1% because the ageing of society has made households' balance sheets less vulnerable to rate increases.
Find Out More