Surprisingly strong wage data ends NIRP and YCC in Japan
The Bank of Japan (BoJ) decided to end its negative interest rates policy and set the target band for the overnight market rate at 0%-0.1% at Tuesday’s meeting, earlier than our call for April. The first tally of the Spring Wage Negotiation, mainly for leading firms, was surprisingly strong, making the Bank confident about the wage-driven path to its 2% inflation target in coming years.
What you will learn:
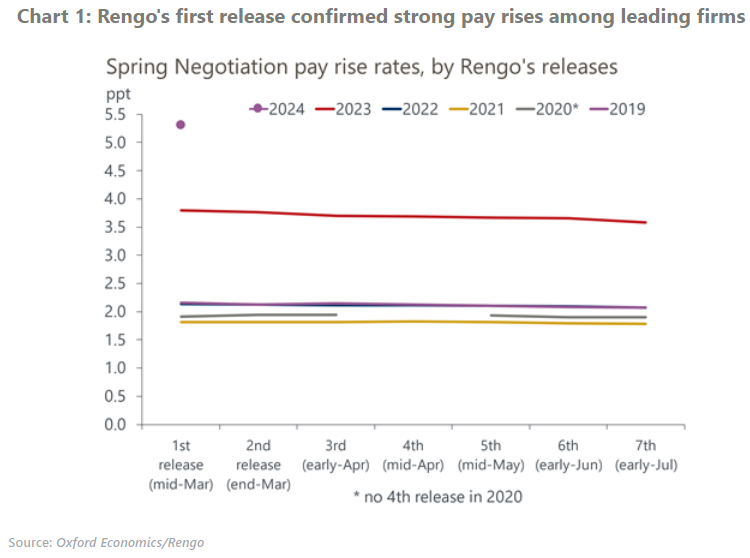
- In the first tally, the headline pay rise rate was 5.3%, much higher than the 3.8% in 2023 and market expectations. As the wage settlement for smaller firms become available, the pay rise rate will likely decline, converging to 4.5% which is the pay rise rate for small firms in the first tally.
- In order to guide market expectation for next policy moves, the policy statement said that “given the current outlook for economic activities and prices, the Bank anticipates accommodative financial condition will be maintained for the time being.” We anticipate the BoJ will maintain an effective zero-interest rate policy at least for another year.
- The BoJ also dismantled the yield curve control framework, which had increasingly become a formality after a decision in October 2023 to make it more flexible. In order to avoid disruptions in long-term yields, the bank commits to keep purchasing Japanese government bonds (JGB) close to its current pace for now, and promises to intensely increase them upon sharp yield rises.
- While committing to continue a quantitative easing (QE) policy through JGB purchases, the BoJ decided to formally end the purchase of risky assets such as ETFs and REITs which have not taken place for several months. We believe that the BoJ will come up with a comprehensive exit strategy from QE policy later this year after its ongoing policy review.
Tags:
Related Posts

Post
How Asia’s supply chains are changing | Techonomics Talks
Global supply chains have continued to expand, despite talk of deglobalization and nearshoring. US and Japan have started to de-couple from China, but other G7 countries grow more dependent on Chinese inputs. Several "hotspots" are emerging across Asia with multiple winning formulas.
Find Out More
Post
BoJ to raise its policy rate cautiously to 1% by 2028
We now project that the Bank of Japan will start to raise its policy rate next spring assuming another robust wage settlement at the Spring Negotiation. If inflation remains on a path towards 2%, the BoJ will likely raise rates cautiously to a terminal rate of around 1% in 2028.
Find Out More
Post
Japan inflation to rise to 1.8%, but downside risks are high
Reflecting a surprisingly strong Spring Negotiation result and weaker yen assumption, we have upgraded our baseline wage and inflation forecasts. We now project higher wage settlements will push inflation towards 1.8% by 2027. Uncertainty is high, however.
Find Out More