Japan: The impact of structural labour shortages on inflation

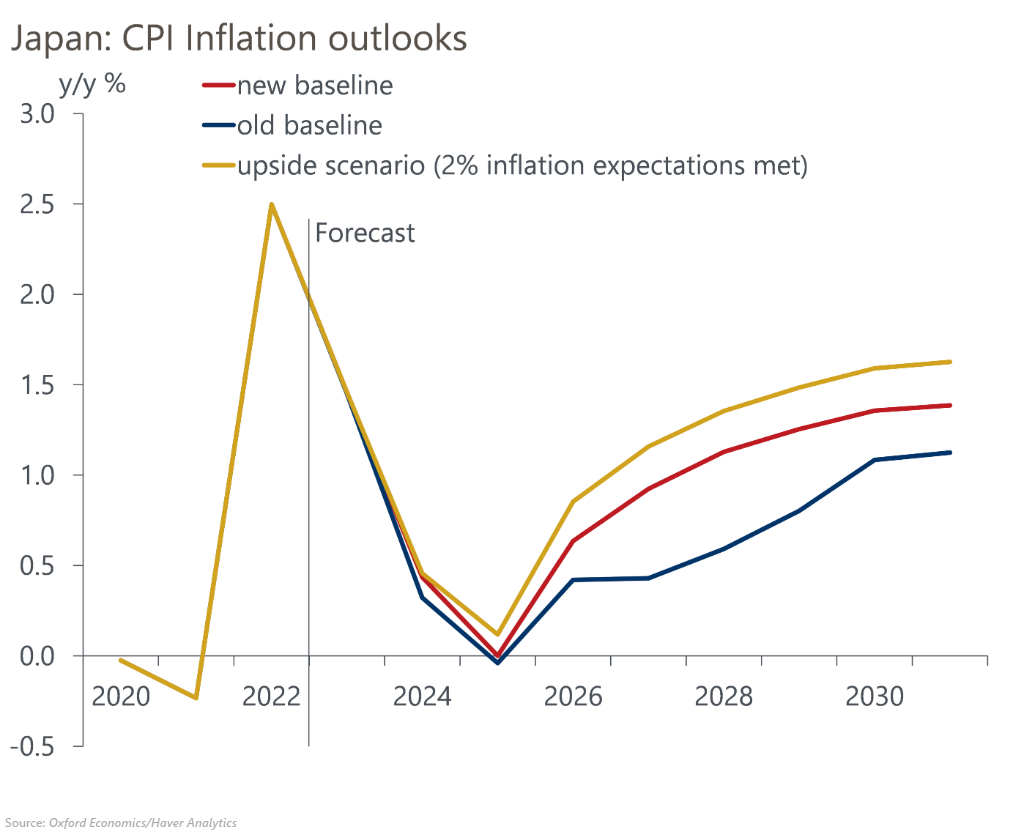
We have revised up our long-term wage and inflation projections based on a larger impact from structural labour shortages due to adverse demographic trends. Even after raising our wage growth assumptions by 0.5ppts on average over 2024-2030, however, we still forecast inflation only reaching 1.4% in 2030 – well short of the 2% target.
What you will learn:
- We now project higher base-wage increases for regular workers. We assume that wage growth set in the annual spring negotiations will rise gradually to 3% by 2030 from an average of 2.3% in the five years before the pandemic. Despite the rising need for wage increases to secure talented workers, Japan’s rigid employment system will constrain pay growth.
- We also revised up our projection for the hourly wage for part-time workers, which is more elastic to labour market conditions than wages for regular workers. We project hourly wages to increase as fast as in the late 2010s this year and then to accelerate, reaching close to 4% by 2030 due to the limited pool of additional labour supply.
- Gradual but persistent wage rises will boost inflation expectations accordingly. Given that Japan’s inflation expectations tend to be formed adaptively, we believe that inflation expectations will rise in accordance with actual price developments. In our baseline, we assume that inflation expectations will rise only gradually to 1.5% in 2030 from 1.1% in 2022.
Tags:
Related posts

Post
Japan’s on course for July rate hike, but risk of June increases
The Bank of Japan (BoJ) kept its policy rate at 0.50% at Wednesday's meeting, as expected. Despite a marginally higher increase in pay than last year at the first round of the spring wage negotiations, our baseline view is for the BoJ to hike its policy rate only gradually due to concerns about the capacity of small firms to raise wages and the lacklustre rate of consumption.
Find Out More
Post
Japan’s supply-driven food inflation to persist longer than expected
We have revised our CPI forecast upwards for this year and next, due to more persistent supply side-driven food inflation, led by soaring prices of rice. Despite the significant revision to the short-term inflation path, we don't expect the Bank of Japan (BoJ) to react with a rate hike.
Find Out More
Post
Japan’s older households to support spending under higher rates
The resilience of consumption is essential to support sustained wage-driven inflation and the Bank of Japan's rate hikes. We see little risk of spending faltering due to the projected gradual rate hikes to 1% because the ageing of society has made households' balance sheets less vulnerable to rate increases.
Find Out More