The path of monetary policy will shape the growth outlook of Indonesia
Indonesia’s domestic demand has proved surprisingly resilient to monetary tightening in 2023, prompting multiple upgrades to our growth forecast this year. However, we still expect the impact of monetary tightening will feed through to growth eventually.
What you will learn:
- Two key shifts will influence the monetary policy path in 2024. Indonesia’s current account dipped into deficit in Q2, and we don’t expect it to revert to surplus anytime soon. Lower commodity prices, as well as the contrasting picture between relatively resilient domestic demand and a soft external sector will suppress the external balance.
- Meanwhile, the pace of rupiah weakening might moderate, but we expect the depreciating trend to continue. While the rupiah has bounced back a little in the last month, we suspect the main driver – lower US yields – will partly reverse given market pricing for rate cuts in the US is likely overdone.
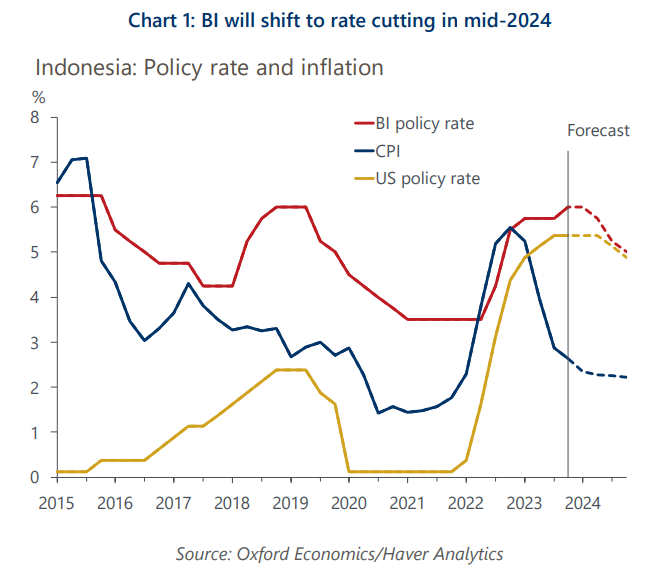
- After a surprise hike in October, Bank Indonesia stayed put in November and we think will remain on hold for some time.
- We think Indonesia’s growth will remain below-trend in 2024 given the impact from past monetary tightening and a weak global economic backdrop.
Tags:
Related Posts

Post
How Asia’s supply chains are changing | Techonomics Talks
Global supply chains have continued to expand, despite talk of deglobalization and nearshoring. US and Japan have started to de-couple from China, but other G7 countries grow more dependent on Chinese inputs. Several "hotspots" are emerging across Asia with multiple winning formulas.
Find Out More
Post
Indonesia rate cuts will bolster credit demand, with pockets of risks
We forecast Bank Indonesia will start cutting its policy rate in Q2, which will provide a cyclical tailwind for credit growth and consequently domestic demand, as lower real lending rates will help boost loan demand.
Find Out More
Post
The costs and eventual benefits of smooth decarbonisation in ASEAN
Reaching net zero carbon emissions by 2050 would likely have a larger impact on economic activity initially in ASEAN5 countries than more gradual decarbonisation. But our modelling suggests the gap would narrow in later years and turn positive in most places approaching 2050.
Find Out More