Six lessons from the US-China trade war as the next phase looms
With further tariff increases on US imports from China effective from August 1st, 2024 and potentially more to come after November’s US presidential election, we take this opportunity to examine the implications and outlook of the US-China trade war.
What you will learn:
- US tariffs have cut imports from China by 35%-40% relative to plausible counterfactual paths, and the impact has risen over time. We estimate a 1ppt rise in US tariffs cuts imports from China by 2.5% in the long term, meaning the high tariffs now being discussed in the US would be prohibitive.
- Suppliers in NAFTA and other Asian economies have stepped into the gaps left by China. This may encourage additional US protectionism versus China. Evidence of some Chinese goods being re-routed into the US to evade tariffs, meanwhile, may see third countries being targeted as well.
- US tariffs have not shrunk its overall trade deficit even if the deficit with China has shrunk. Trade conflict has cut US GDP by an estimated 0.2%-0.4% and raised prices by 0.1%-0.3%.
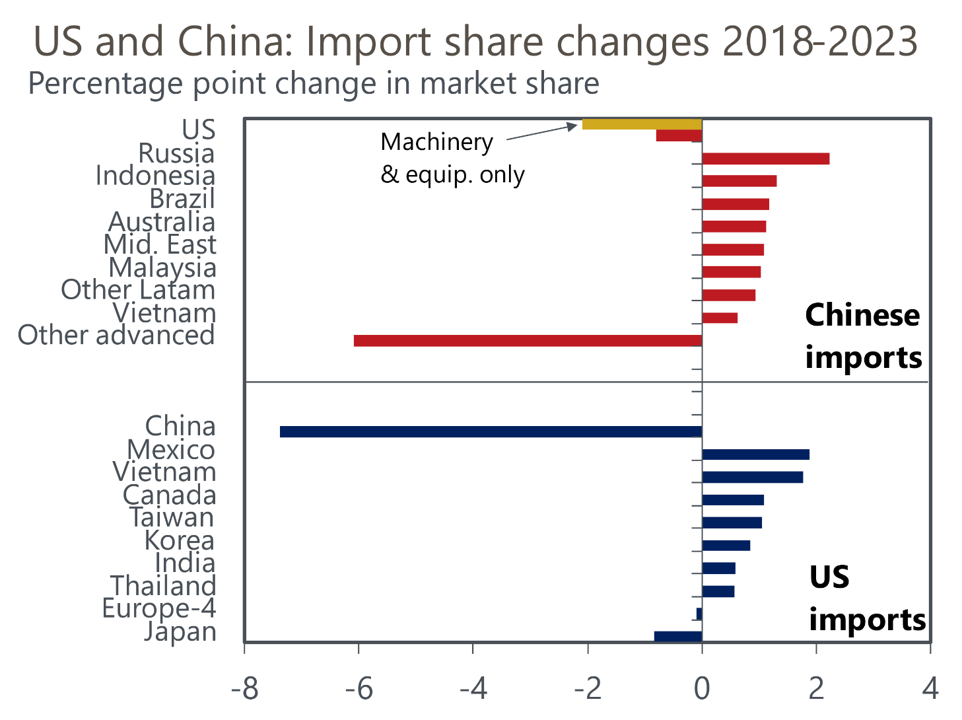
*Europe 4: Germany, France, UK, and Italy
Tags:
Related Resources

Post
Tariffs and Their Global Impact: A Note from the Desk of our Chief Economist
On 2 April 2025, the US Administration announced a set of tariff increases, bringing the US back to levels of protectionism last seen in the Great Depression era. This significant shift in trade policy is set to have far-reaching implications for the global economy.
Find Out More
Post
Initial takeaways from Trump’s ‘Liberation Day’ announcement
In two or three years' time, US imports could fall by around 15% due to discounted reciprocal tariff hikes.
Find Out More
Post
Trump tariff turbulence threatens global industrial landscape
Trump has moved swiftly to advance a trade agenda that goes beyond what was promised in the campaign. This will have a major impact on global industrial prospects.
Find Out More