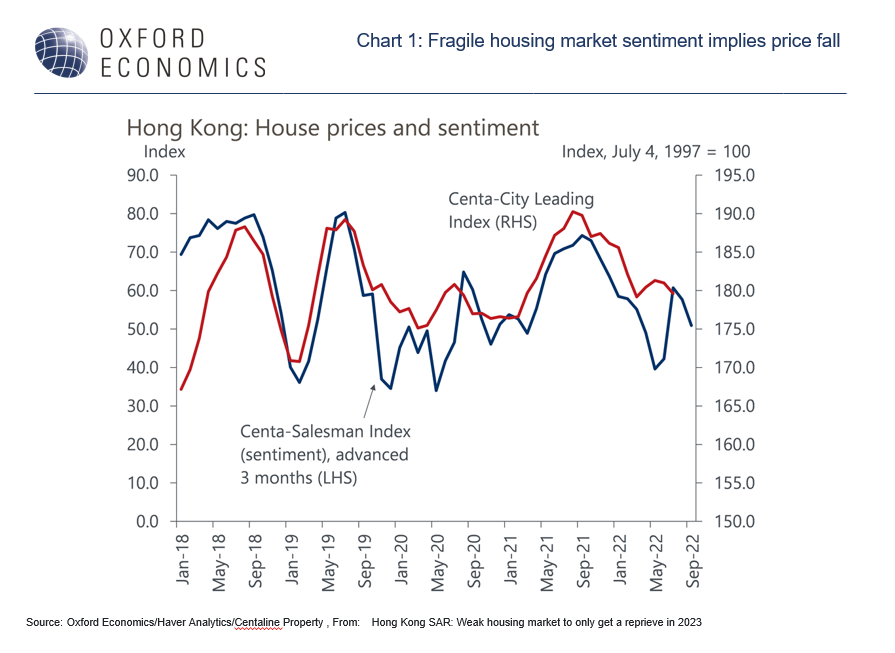
Hong Kong’s weak housing market to only get a reprieve in 2023
Hong Kong’s housing market sentiment weakened during H1 2022, reflecting a resurgence of Covid infections in Q1 and a weak domestic economic outlook. House prices in the secondary market fell 2.8% in Q2 versus Q4 2021. And this housing market weakness may not be over yet.
What you will learn:
- As an international trade and financial centre in Asia, changes in Hong Kong’s external environment have an
outsized impact on its domestic economy, and hence on its housing market. - We expect residential property prices to fall by about 4% y/y in Q4 2022, mainly due to the gloomy economic outlook. Slow border reopening progress and challenges to the external environment have severely dampened local sentiment.
- Higher mortgage rates will also play a role in deterring lower income households from buying property and weigh on residential property investment demand.
Tags:
Related posts

Post
Japan’s fiscal policy will remain loose, which increases risks to debt sustainabilit
We've changed our fiscal outlook for Japan in our December forecast round. We now expect the new government to set a primary deficit close to that of 2024, at 2%-3% of GDP for 2025-2027, instead of restoring a balanced budget by taking advantage of strong tax revenue. We assume higher bond yields will force the government to take measures to reduce the deficit from 2028.
Find Out More
Post
A reality check on the status of RMB internationalisation
The recent geopolitical shocks and abrupt US policy shifts have heightened concerns about the stability of the dollar-centric global financial system and strengthened the perceived need for diversification.
Find Out More
Post
The rise of Southern India’s business service hubs
Over the next five years, India is set to be one of the fastest-growing major economies across Asia Pacific, lead by the performance of its IT and business services. The Southern states of Karnataka and Telangana are at the forefront of this success as they are home to two of India’s most rapidly growing cities and productive cities—Bengaluru and Hyderabad.
Find Out More