Global Industry: Energy transition will transform mining—promise and pitfalls
We expect that demand for energy transition-related critical minerals will grow significantly in the next decades even in the absence of rapid progress required to achieve net zero. The IEA estimates that total demand for key minerals including lithium, copper, nickel, and cobalt will more than double by 2050 if the world continues with currently stated policies and increase fourfold in a net zero scenario. This represents tens of thousands of kilotons (kt) of extraction.
What you will learn:
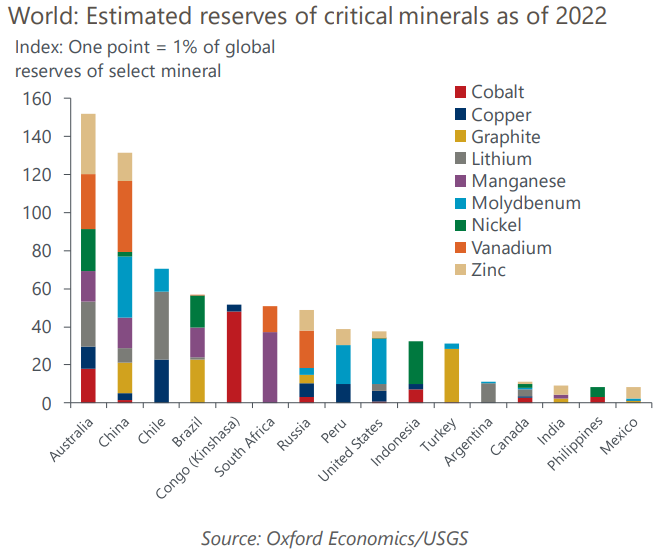
- Many critical minerals are concentrated in specific regions. Australia, China, Chile, Russia, and Brazil have high proportions of total global reserves for several key minerals, while DR Congo, South Africa, Indonesia, and others have large concentrations of one or two. Tapping into the demand for these metals could help many countries that rely on fossil fuels for economic activity to make up for declining fossil fuel related extraction.
- Indonesia has shown how countries can try to leverage a large stock of a critical minerals into wider economic gains—a ban on raw nickel exports has allowed it to locate more value-added economic activity within the country. Despite the risks of a protectionist approach, other countries will likely try to follow, but Indonesia’s combination of relatively stronger governance and an extraordinarily high share of nickel production and reserves are not easily replicable.
- There are however various downside risks: metals recycling, technological breakthroughs, and substitution could cut the potential demand increases for critical minerals. Social, economic, and environmental disruptions from mining or refining projects can also jeopardise the political consensus needed for these kinds of investments. Many of the countries endowed with large reserves of critical minerals have poor governance, poor environmental track records,
Tags:
Related Research

Post
Oxford Economics enhances its Commodity Price Forecasts coverage
Oxford Economics expands Commodity Price Forecasts service to include battery metals, agricultural commodities and plastics.
Find Out More
Post
The socio-economic impact of TikTok in Australia
This report provides the results of our economic modelling of TikTok’s economic contribution to the Australian economy, as well as the findings of survey research into TikTok’s users and Australian businesses. It looks at the real world impacts users report as well as the diversity of TikTok’s online communities.
Find Out More
Post
Why we believe the industry cycle in the Eurozone is finally turning
Even though incoming hard data on eurozone industry is still downbeat, leading indicators suggest that we're at a turning point. We expect favourable cyclical and structural tailwinds will now take over, and industry output to accelerate through this year to 2% y/y growth by Q4.
Find Out More