EV shift could pose a big challenge to Japanese economy
Amid the fast-progressing electric vehicle (EV) shift, maintaining high competitiveness in auto-related sectors and ensuring a smooth labour transition across industries are crucial for the growth of the Japanese economy. As auto production shifts towards EVs, which require different inputs from traditional internal combustion engine cars, parts suppliers will need to adapt to avoid losing market share to foreign players. Change in automotive supply chains would also require workers to move across different industries, a task particularly challenging for Japan.
What you will learn:
- The Japanese economy is reliant on the auto industry, as the sector accounts for 15% of industrial production. Furthermore, the sector has one of the highest multiplier effects, given breadth and depth of its supply chains. Spillover effects are seen not just in auto parts, but also among commerce, plastics, electronics, and metal industries.
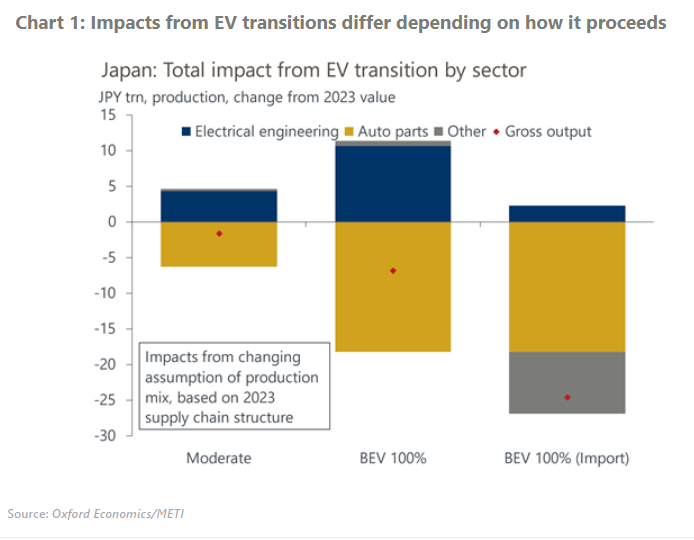
- The EV transition would bring about a huge change to the current supply chain structure. While demand for parts like electric motors and lithium-ion batteries will increase, there would be less demand for engines and transmissions. Our analysis reveals that the economy will be hit as EV transition proceeds, but the magnitude will depend on the nature of the transition.
- There would be a limited impact if hybrid vehicles retain as high a share of production as the Japanese government currently expects. However, if the entire auto production shifts to battery EVs, Japanese gross nominal output would be 0.6% lower than the 2023 level.
- Because the EV transition will reshape the industry structure, a smooth reallocation of labour across industries is imperative for the transition to work. Otherwise, capacity of EV goods providers will be strained, potentially raising the import dependency of the sector. We simulated a scenario where a considerable part of the input for battery EVs is sourced from abroad, in which case 2.2% of Japan’s gross nominal output and 1.1% of total employment will be lost.
Tags:
Related Posts

Post
25% auto tariffs especially painful in Japan and South Korea
US tariffs of 25% on all automobile and auto parts will weigh heavily on the Japanese and South Korean automotive sectors. A GTAP analysis suggests Japanese and South Korean automotive production will each shrink by approximately 7%. The impact is larger than suggested by bilateral trade data, because vehicles assembled in other countries before being shipped to the US will also be affected, dampening domestic auto parts production.
Find Out More
Post
‘Liberation Day’ 24% tariff will limit Japan’s growth
The 'Liberation Day' tariffs, together with separately announced higher tariffs on auto imports to the US, will lead us to cut our growth forecast for Japan. The direct impact of the tariffs will end the modest growth we projected in March, and we now think the economy will barely grow in 2025-2026. This initial estimate does not consider the indirect impact from high trade policy uncertainty and retaliation from other economies.
Find Out More
Post
Japan’s on course for July rate hike, but risk of June increases
The Bank of Japan (BoJ) kept its policy rate at 0.50% at Wednesday's meeting, as expected. Despite a marginally higher increase in pay than last year at the first round of the spring wage negotiations, our baseline view is for the BoJ to hike its policy rate only gradually due to concerns about the capacity of small firms to raise wages and the lacklustre rate of consumption.
Find Out More