China’s demographic shift poses tough economic and fiscal challenges
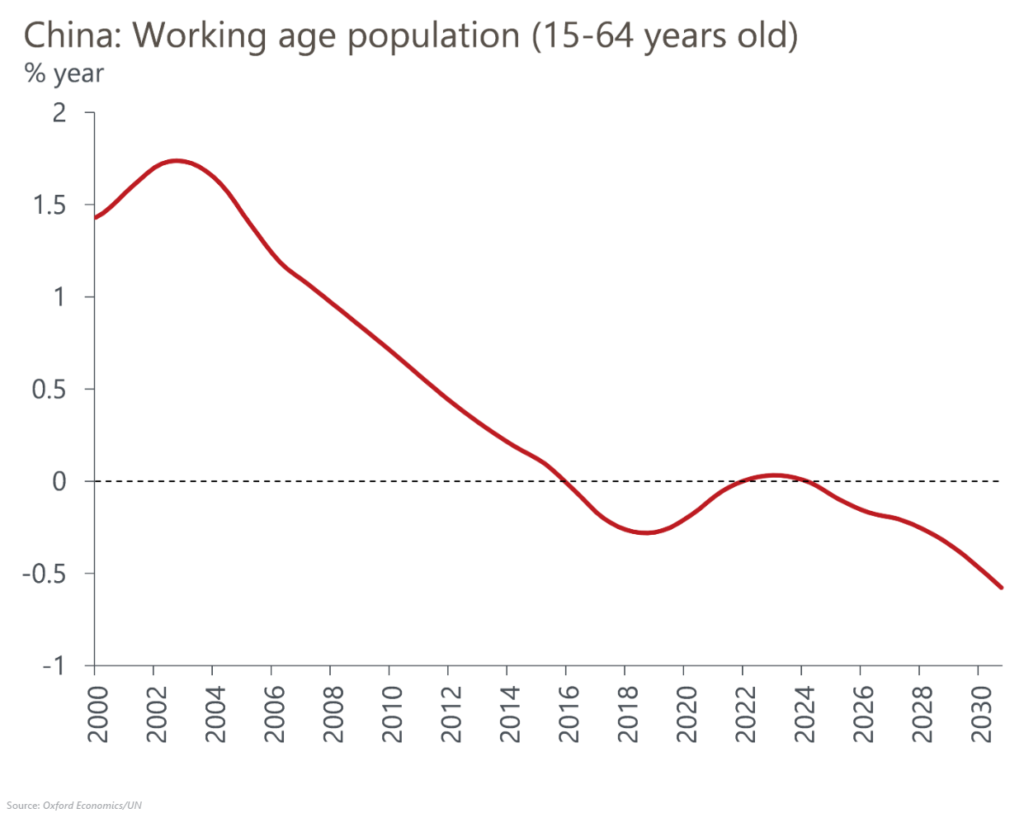
China is undergoing a demographic transition that implies downward pressure on labour supply and economic growth over the coming decades. Based on the latest data from the National Bureau of Statistics, mainland China’s population fell 850,000 to 1.41bn in 2022 – the first decline in 60 years. The number of births fell to a new low of 9.6mn in 2022, down from 10.6mn in 2021, and was outpaced by the 10.4mn deaths recorded in 2022, up from 10.1mn in 2021, partly related to Covid infections.
What you will learn:
- In the near-term, we expect the labour participation rate will recover as the country reopens and activity normalises. But this will not be enough to fully offset the effects of an ageing population on the size of the working-age population, and we expect the decline in labour supply growth will deepen in the coming decades.
- A shrinking labour force will widen the pension gap, weakening the social safety net. This could keep savings rates high, hindering the government’s rebalancing efforts towards a consumer-driven economy. The fiscal implications are also negative, as the fiscal space for a response to any future crisis will be constrained, particularly as local government debt levels are already elevated.
- The worsening demographics will be a drag on growth, leaving the economy reliant on investment and productivity. However, returns on investment are declining, while productivity is being challenged by the international threats of technological decoupling and supply-chain diversification. We forecast China’s GDP growth will slow to an annual average of around 4.5% this decade, from 7.7% per year in 2010-2019.
Tags:
Related Resouces

Post
The latest export from China is … deflation
We expect Chinese export price deflation to provide a helpful tailwind in the struggle to bring EM inflation back to target.
Find Out More
Post
How Asia’s supply chains are changing | Techonomics Talks
Global supply chains have continued to expand, despite talk of deglobalization and nearshoring. US and Japan have started to de-couple from China, but other G7 countries grow more dependent on Chinese inputs. Several "hotspots" are emerging across Asia with multiple winning formulas.
Find Out More
Post
China decoupling – how far, how fast?
Economic decoupling from China is ongoing, but the latest evidence suggests that, especially outside the US, the process is gradual and piecemeal. Trade decoupling may be slowly spreading from the US to other advanced economies, however surveys suggest foreign investors' attitudes to China improved slightly in 2023, though they are still more negative than a few years ago.
Find Out More